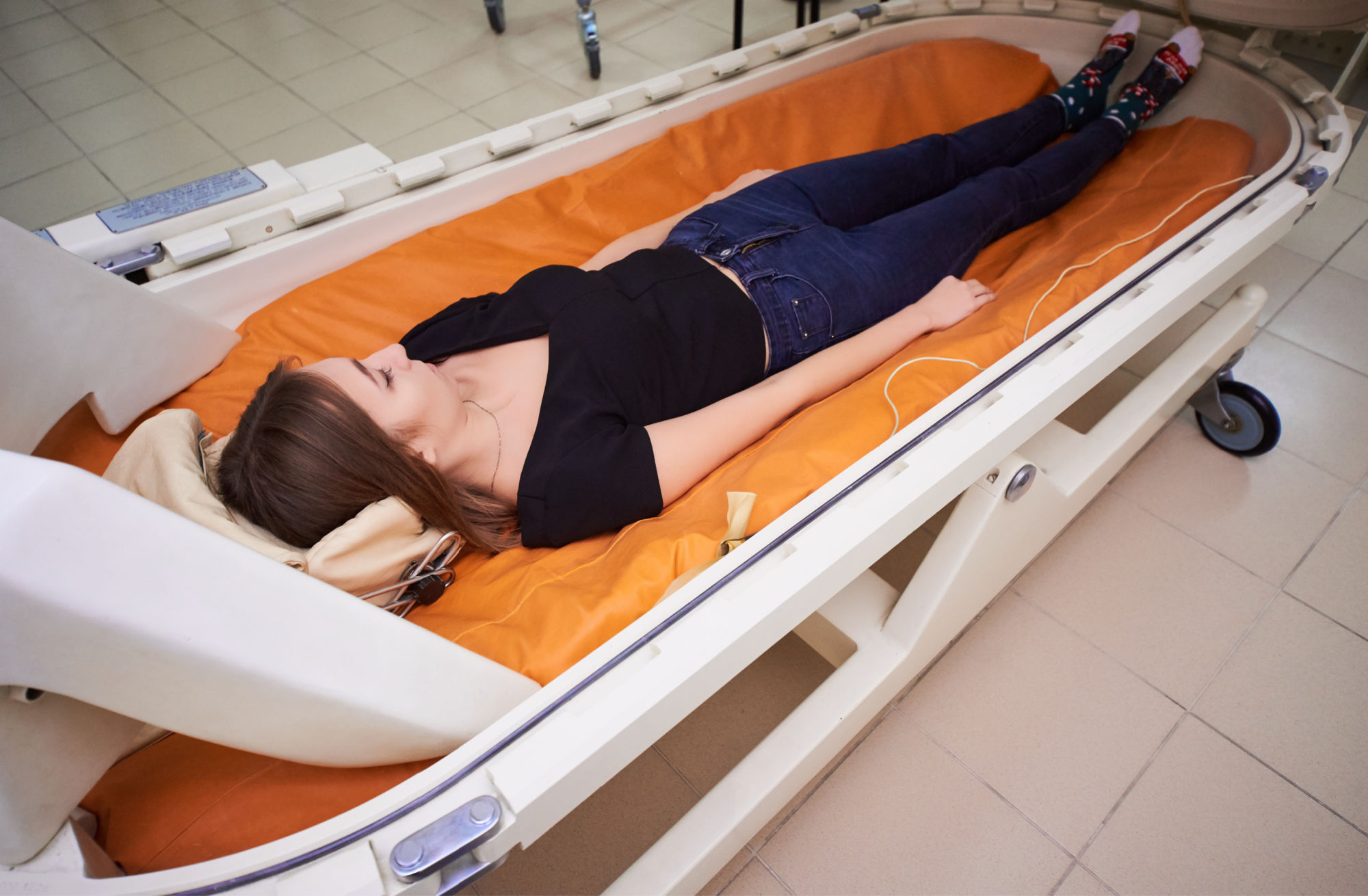
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a specialized treatment designed to increase the amount of oxygen your body can carry. This process involves breathing pure oxygen in a controlled, pressurized environment, such as a chamber. The pressurized conditions allow your lungs to gather more oxygen than would be possible under normal atmospheric pressure. This influx of oxygen can have significant therapeutic benefits, particularly for certain medical conditions or wound care where increasing tissue oxygen levels is essential for healing.
The concept behind hyperbaric medicine is rooted in the fundamental role oxygen plays in health and healing. By delivering oxygen at concentrations much higher than atmospheric levels, HBOT aims to bolster the body’s natural healing processes. It’s most commonly associated with treating decompression sickness (a hazard of scuba diving). Still, its scope extends to a variety of conditions, such as serious infections, bubbles of air in your blood vessels, and wounds that may not heal as a result of diabetes or radiation injury. By enhancing the body’s oxygen supply, HBOT supports the fight against infection, stimulates the growth of new blood vessels, and promotes the repair of damaged tissues.
Our providers, Dr. Maressa Alejandro, MD, and Nurse Practitioner Sharon Caravetta, FNP, will take into account your age, medical history, and the specific health issue that may benefit from oxygen therapy to create a tailored treatment plan.
Fundamentals of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) leverages increased air pressure and high oxygen concentration to accelerate your body’s natural healing processes.
Concept and Mechanism
The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy exposes you to pure oxygen at pressures higher than normal air pressure. This pressurized environment enables your lungs to gather more oxygen than would be possible at normal air pressure. Your blood carries this extra oxygen throughout your body, helping to fight bacteria and promote the release of growth factors and stem cells, which foster healing.
Medical Indications and Therapeutic Uses of the Hyperbaric Chamber
HBOT Treatment enhances your body’s natural healing process by inhalation of 100% oxygen in a total body chamber, where atmospheric pressure is controlled and increased. It is used to treat a variety of medical conditions and is known for accelerating wound healing and treating life-threatening infections.
Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
Your body requires adequate oxygen to heal wounds effectively. The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be particularly beneficial for non healing wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, by enhancing oxygen delivery to damaged tissues. It promotes angiogenesis and the formation of new blood vessels and, therefore, improves blood flow to the affected area. This process is pivotal in wound healing and the survival of skin grafts and flaps.
– Complications: HBOT helps mitigate complications that occur due to wound healing issues like infections or tissue death.
– Anemia: Even in cases of severe anemia, where blood’s capacity to carry oxygen is impaired, HBOT can saturate tissues with oxygen directly.
Treatment of Decompression Sickness and Air or Gas Embolism
Decompression sickness (DCS), often associated with scuba diving, occurs when you experience a rapid decrease in pressure, causing gasses dissolved in your blood to form bubbles. This can affect your blood, tissues, and organs. HBOT can be an effective treatment as it reduces the size of the gas bubbles and improves oxygenation to tissues.
– Arterial Gas Embolism (AGE): Prompt HBOT can be life-saving in cases of AGE, where bubbles enter your blood vessels and block blood flow.
Management of Poisoning and Infections
HBOT plays a critical role in the management of certain poisonings and infections. The high levels of oxygen delivered during therapy can halt the growth of and kill certain bacteria, such as those causing gas gangrene and actinomycosis.
– Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: By displacing carbon monoxide from the hemoglobin molecules, HBOT quickly restores the blood’s ability to carry oxygen.
– Osteomyelitis: Chronic bone infection, or osteomyelitis, is an example where HBOT supports the body’s immune system and enhances the efficacy of antibiotics.
– Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Oxygen under pressure helps in reducing toxins produced by certain bacteria, preventing tissue death, and can stop the progression of diseases like gangrene.
It is important to consult a medical professional to determine whether HBOT is suitable for your specific medical condition. This therapy is typically considered when conventional treatments have not yielded satisfactory results or when substantial research supports the use of HBOT for a particular indication.
Technical and Procedural Aspects
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves carefully controlled use of oxygen at elevated pressures. Understanding the operational procedures and session logistics is crucial for both safety and therapeutic efficacy.
Operational Procedures and Safety During Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy uses a specialized chamber that is pressurized. Safety precautions are paramount to prevent risks such as fire hazards, as oxygen-rich environments can turn everyday objects like lighters and battery-powered devices into potential ignition sources. Prior to entering an HBOT chamber, you’ll be instructed to remove such items.
– Healthcare Provider Guidelines: A healthcare provider will review safety precautions with you. This includes checking for prohibited items and ensuring you understand the procedures.
Safety Precautions Inside the Chamber:
– Fire Hazard Mitigation: Absolutely no flammable materials are allowed inside.
– Monitoring Devices: Electronic medical devices must be specifically approved for use in the hyperbaric environment.
Ears and sinuses may experience pressure changes during therapy, and specific techniques are taught to manage this discomfort. It is also essential for patients with diabetes to check blood sugar levels before and after sessions, as fluctuations can occur.
Session Dynamics and Treatment Planning for Maximum Benefit from HBOT
– Preparatory Measures: You may be required to wear a clear hood or mask to breathe the oxygen, which ensures 100% oxygen saturation.
– Monitoring Parameters: Blood pressure and pulse are typically monitored throughout the session.
Sessions typically last for 90 to 120 minutes, with the chamber gradually brought to therapeutic pressure levels. These specifics should form part of a comprehensive treatment plan designed by a healthcare provider tailored to address conditions such as radiation injury, stroke, or soft tissue post-surgical trauma. HBOT aims to enhance the body’s natural healing processes by saturating blood and cells with oxygen, reducing ROS (reactive oxygen species), and improving recovery.
Patients may feel side effects such as tiredness or a feeling comparable to the sensation of ascent in flight (ear fullness). More severe but uncommon risks include embolism. Therefore, it’s vital to communicate any discomfort to the attending healthcare professional immediately. Precautions are particularly important if you’ve recently had surgery or have a history of certain medical conditions.
Each session’s parameters are carefully determined by your healthcare provider based on your specific needs, ensuring treatment is not only effective but also administered with the utmost care for your health and safety.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is generally considered safe.
Common Challenges and Management
– Ear and Sinus Pressure: As you undergo HBOT, you may experience pressure in your ears and sinuses similar to the sensation felt during an airplane’s descent. This is due to the pressurization in the treatment chamber. To alleviate discomfort, techniques such as yawning or swallowing can help equalize ear pressure.
-Vision Changes: Mild short-sightedness (myopia) may occur as a temporary side effect due to eye lens changes. These vision changes typically revert back after treatment ceases.
– Barotrauma: Middle ear injuries can result if pressure is not equalized properly. Wearing an ear mask and employing pressure-equalizing maneuvers are standard management practices.
How to Manage:
– Practice swallowing or yawning to relieve ear pressure.
– Take breaks between treatments if mild vision changes occur.
– Use ear protection and follow instructions carefully to prevent barotrauma.
Contraindications:
– Prior history of ear surgery or ear flaps in place may preclude you from undergoing HBOT.
– If you have uncontrolled seizures or certain respiratory conditions, HBOT might not be suitable for you.
– Usage of certain medications, like some types of insulin or skin care products, might affect your suitability for HBOT.
Always discuss your medical history and current health conditions with our physicians to understand the potential risks and determine if hyperbaric oxygen therapy is appropriate for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment. This specialized treatment can significantly impact various medical conditions. Below are answers to common questions you might have about HBOT.
What are the potential benefits of undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Undergoing HBOT can increase the amount of oxygen your blood can carry, which helps promote healing, fight bacteria, and stimulate the release of growth factors and stem cells. It is especially effective in accelerating the healing of wounds and infection control and may reverse mild traumatic brain injury and concussion.
How long do the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy typically last?
The duration of HBOT’s effects varies depending on the condition being treated. Some patients experience long-term benefits, while others may need ongoing treatments for chronic conditions. It’s important to consult with our providers, Dr. Alejandro and Shaon, FNP for specifics about your situation.
What conditions are commonly treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used for various approved indications like air or gas embolism, carbon monoxide poisoning, and chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers. It is also utilized for recovery from radiation injuries and certain types of infections, pre and post-surgery to speed up the healing process, TBI, concussion, fibromyalgia, and PTSD, among many other conditions.
Who may not be suitable candidates for hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Individuals with certain types of lung diseases, a history of ear surgery, or certain types of seizures may not be suitable for HBOT. Consultation with medical professionals is necessary to assess the risks and determine suitability.
What does research say about the efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Research indicates that HBOT is effective for its approved uses and can be beneficial when properly administered. It’s important to seek treatment at accredited medical facilities to ensure the use of evidence-based protocols.